Swollen Head Syndrome in poultry (APV) is caused by a virus and currently, there is no specific treatment. The disease causes significant damage in poultry farming, with a high infection rate of up to 100%. The disease has a high mortality rate due to infection APV with other diseases such E.Coli, Salmonella, Mycoplasma, etc, APV (Swollen Head Syndrome) in poultry is a difficult disease to diagnose and to understand clearly about APV and learn effective disease prevention and management procedures , please follow below article.
The cause of Avian Pneumovirus (APV)
Swollen head syndrome in chickens (APV) is caused by the Avian pneumovirus, an RNA virus that primarily affects the respiratory system of chickens, especially turkeys. APV is transmitted through the respiratory route, and the disease outbreaks are particularly severe when there are high levels of toxic gases and odors in the poultry house, such as CO2, NH3, H2S.
The symptoms of APV (Avian Pneumovirus)
- Slow-growing chicken, reduced appetite, lethargy, rough and scruffy feathers.
- Eyes with foamy discharge, teary eyes -> This is one of the characteristic symptoms of a disease.
- Difficult breathing, rapid breathing, audible wheezing in the trachea.
- Chicken with nasal inflammation, runny nose.
- Swollen face and head, head shaking, swelling of the scalp
- Chickens can experience paralysis and wry neck.
- Severe cases are when APV combined with E.Coli causes head edema syndrome (Swelling of the head syndrome - SHS). This syndrome is seen in chickens over 1 month old with typical neurological and respiratory symptoms such as: Chickens have trouble walking, wry neck, shaking head, edema of head, face and eyes.
- Egg laying issues: Broken, shrunken, deformed egg shells, thin and pale-colored shells, a reduction in egg production by 5-30%.
- Breeding chickens: reduce 5-10% hatch rate
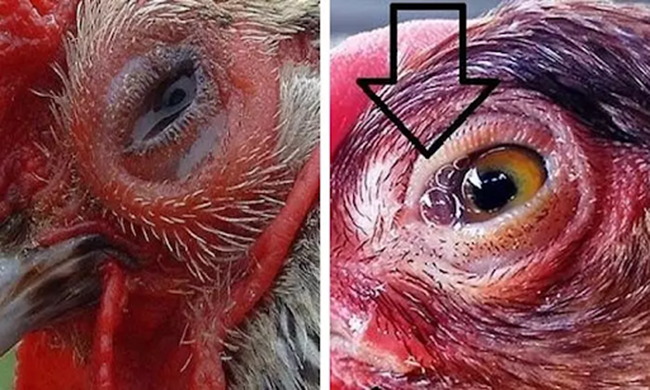
Image 1: Foamy discharge, teary eyes.
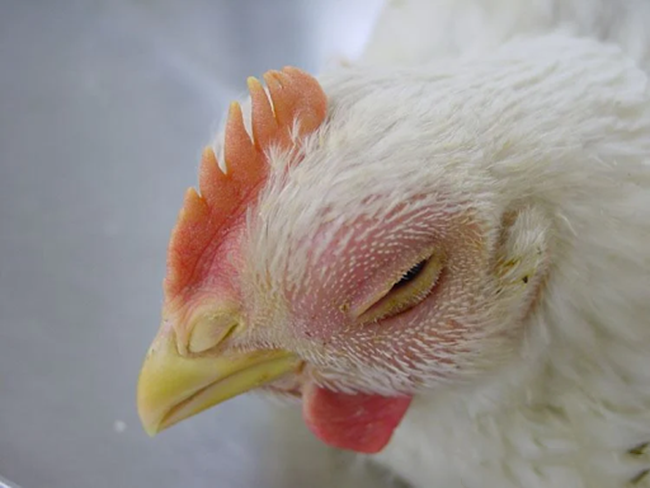

Image 2: Chicken with swollen face and head.
The Consequences of APV
- Inflamed eyelids, blindness, inflammation and formation of yellow Fibrin layer beneath the skin of the head and cheeks.
- Trachea with mucus-like fluid but no bleeding. In severe cases of Avian Pneumovirus (APV) infection in chickens, there may be bleeding at the end of the trachea.
- Egg laying hens: Eggshell susceptibility to damage, fragile underdeveloped eggs, leading to oviduct inflammation.
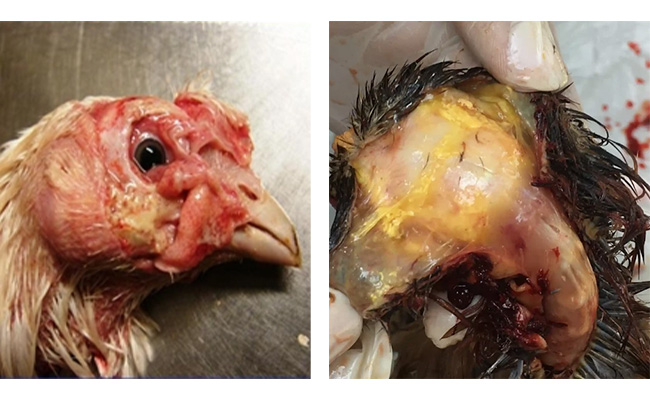
Image 3: Formation of yellow Fibrin layer beneath the skin of the head and cheeks.
Effectively prevent avian pneumovirus (apv) infection in chickens
- Keep the animal pens well-ventilated, maintain a reasonable stocking density, and perform regular disinfection once a week using premium POVIDINE-10% solution at a dosage of 10ml/3 liters of water.
- Prevent diseases by using vaccines according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Regularly enhance immunity: Use GARLIC AMINO at a dosage of 1ml/3-5 liters of water, especially during seasonal transitions. Use B.COMPLEX @ at a dosage of 1g/2 liters of water daily to improve digestion and absorption. Combine with HERBAL ELECTROLYTES GLUCO K+C at a dosage of 1g/2 liters of drinking water to boost immunity and combat stress.
To effectively manage APV (Avian Pneumovirus) disease
APV (Avian Pneumovirus) is a viral disease, so there is no specific treatment for it. Therefore, the focus should be on managing symptoms, boosting immunity, and using antibiotics to treat secondary infections.
Step 1: Isolate all sick birds, and move them to a separate designated area.
Step 2: Thoroughly clean and disinfect the entire area inside and around the poultry coop using G-OMNICIDE or G-ALDEKOL DES FF. Also, clean and disinfect all farming equipment.
Step 3: Treat the symptoms.
- Use an expectorant to reduce cough and phlegm: BROMHEXIN 10 (1g/7-10kg body weight) or BROM-MENTHOL (1ml/ 4-8 liters of drinking water).
- If the animal has a fever, use a fever-reducing medication such as PARA-C (1g /4-6kg body weight) or ANAGIN-C (2-4g/1 liter of water). Administer the medication continuously until the fever subsides.
Step 4: Reinforce the APV vaccination.
You can administer the vaccine at a dosage that is 1.5 to 2 times the standard amount. The intranasal route is preferred for administration.
Step 5: Use prophylactic antibiotics to prevent secondary infections and boost the immune system of the flock.
Regimen 1:
- Morning: Administer TIMICOSIN-2500G orally at a dosage of 1ml/12kg of body weight.
- Afternoon: Administer ENRO 20 orally at a dosage of 1ml/4 liters of water.
In addition, it is necessary to boost the immune system of the flock. Use the following solution to enhance immunity: ELECTRO GLUCO KC + STRONG LIVER + HIGH GLUCAN GARLIC at a dosage of 1ml/2 liters of water.
Treatment duration: 5-7 days.
Regimen 2:
- Morning: Administer DOXY-Z500 orally at a dosage of 1g/50 kg of body weight
- Afternoon: Administer FLOR 200 orally at a dosage of 1ml/10kg of body weight.
In addition, it is necessary to boost the immune system of the flock: HERBAL ELECTROLYTES GLUCO K+C (1g/1 liter of water) + SORBITOL B12 (1g/1-2 liters of water) + LACTIC (1g/1-1.5 liters of water).
Treatment duration: 5-7 days.
Regimen 3:
- Morning: Administer TIALOR orally at a dosage of 1g/5-7kg of body weight
- Afternoon: Administer FLUMEQUIN orally at a dosage of 1g/5-6kg of body weight.
In addition, it is necessary to boost the immune system of the flock: HERBAL GLUCO K-C (2g/1 liters of water) + SORBITOL B12 (1g/1-2 liters of water) + B.COMPLEX @ (1g/2 liters of water)
Treatment duration: 5-7 days.
Regimen 4:
- Morning: Administer TYLOSIN 500 orally at a dosage of 1g/25-30kg of body weight
- Afternoon: Administer AMOX-S 500 orally at a dosage of 1g/30kg of body weight.
In addition, it is necessary to boost the immune system of the flock: VITAMIN C 35 (1g/3 liters of water) + SORBITOL B12 (1g/1-2 liters
of water) + NH-ADE-B.COMPLEX (1g/3-4 liters of water)
Treatment duration: 5-7 days.
Regimen 5:
- Morning: Administer TYLODOX orally at a dosage of 1g/10kg of body weight
- Afternoon: Administer ANTI-DIARRHEA orally at a dosage of 1g/5kg of body weight.
In addition, it is necessary to boost the immune system of the flock: VITAMIN C 15 (1g/1 liters of water) + SORBITOL B12 (1g/1-2 liters of water) + BACILLOZYM @ (1g/2 liters of water)
Treatment duration: 5-7 days.
For severely affected individuals:
Inject Aziflor new (1ml/10kg body weight) in combination with Dexa (1ml/10kg body weight) or Linspec new (1ml/5kg body weight) in combination with Dexa (1ml/10kg body weight).
Note:
- For meat chickens: Add GINSHENG @ NEW (1g/1kg of feed) or GINSHENG NEW (1g/1kg of feed) to the daily diet to promote rapid growth and improve the overall appearance of the flock.
- For laying hens: In order to enhance the reproductive rate and support the recovery of the hens, supplement their diet with ADE-VIT C + CANXI + B12 NEW or SUPPER EGG + STRONG BONE. Administer continuously for 1-2 weeks.
Let’s use effective prevention measures to keep chickens healthy. Hope you become successful farmers!
